Smoking
Dr. Vittorakis Stylianos, MD, PhD
Give yourself a chance to get rid of cigarettes by asking for help at your smoking cessation clinic. You will soon realize that what you thought was impossible is now an easy reality.
It is generally accepted that smoking is one of the leading causes of preventable death in the modern world. Smoking is associated with a number of serious health problems, including cardiovascular diseases, cancer, respiratory and many other diseases. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of these problems and remarkably improve a person's quality of life and life expectancy.
The first preventable cause of death!
Do you know that smoking is the number one preventable cause of death in the modern world?
That is, if we can eliminate it we will save more people a year compared to treating blood pressure, diabetes etc . Every year more than 6 million people die from smoking worldwide and about 24 thousand Greeks.
About 1 out 3 deaths of middle-aged men is due to smoking. It is the cause of conditions that degrade our quality of life, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoporosis, skin ageing (wrinkles), stomach ulcers, sexual impotence, infertility and complications during pregnancy.
According to the World Health Organization, smoking is a disease as it meets the diagnostic criteria of an addictive habit. That is, the smoker has a strong desire and is unable to cut down on the use of cigarettes as he develops withdrawal symptoms at every such attempt, and has a need for more and more use (developing tolerance).
Also for the smoker, smoking takes priority over other pleasures and he or she smokes despite prohibitions, restrictions and evidence of its harmful effects on health. Finally, the associated relapse rates after successful cessation are high.
Stopping smoking on your own is difficult, as nicotine is a powerful addictive substance, similar to heroin and alcohol. But it is not impossible, especially in recent years, when our pharmaceutical quiver has been enriched with new, highly effective, drugs and social vigilance against the scourge of smoking is at its peak.
Why are cigarettes harmful?
Cigarettes contain over 4000 different substances, most of them harmful-toxic to the body. (An estimated 100,000,000,000,000,000,000 oxidating molecules are emitted per inhalation).
Although nicotine is perhaps the most harmless of these substances, it is the cause of addiction and therefore the cause of the difficulty we face in trying to quit. It has been found that by smoking 5 cigarettes a day for 10 days, the brain undergoes such structural changes (at the receptor level) that addiction sets in!
What damage does smoking do to my body? What is smoking guilty of?
About 1 in 3 deaths of middle-aged men is due to smoking.
Smoking causes:
- 87% of lung cancers,
- 30% of other cancers (such as bladder, oesophagus, pancreas,
- larynx, breast, stomach and uterus).
- 14 % of deaths from vascular strokes.
- It is an important cause of death from myocardial infarction.
What harm does smoking cause to my body? (continued)
Smoking also…
- causes infertility in men and women and sexual dysfunction (nicotine is a vasoconstrictor – the well-known Viagra/Cialis are instead vasodilators.
- In pregnancy smoking is implicated in increased risk of spontaneous abortion, pre-eclampsia, prematurity, placental abruption-bleeding, reduced fetal growth.
- It is a cause of sudden infant death syndrome.
- Causes premature menopause, dysmenorrhea (pains during menstruation), premature aging of the skin; wrinkles, grey hair, hair loss, permanent damage to teeth. When yo smoke you smell excessively awful to a non-smoker.
- It is a major cause of chronic cough and the main cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (chronic bronchitis – emphysema) and therefore significant dysfunction – disability. It also increases the severity of asthma and can cause exacerbations of it.
- Smokers have an increased risk of diabetes mellitus, increased risk of stomach ulcers.
Passive (secondary) smoking.
Passive (secondary) smoking is the third most preventable cause of death (after active smoking and alcohol). People who live with smokers are 20% more likely to get lung cancer (here) and twice as likely to have a heart attack. What’s more, the smell that lingers on smokers’ clothes and furniture is not innocent.
It is created by harmful substances that precipitate during smoking. These substances are inhaled even when the smoker is away from home and are equally carcinogenic and harmful, especially for children (tertiary smoking).
Additional Damage that Smoking can Cause
Arterial Blood pressure improvement
Patients who quit smoking gradually reduce or even stop their antihypertensive pills because their blood pressure improves.
Protect your Children
It is a negative role model for our children: If both parents smoke, children have an 80% chance of smoking; if one parent smokes, children have a 50% chance of smoking; if neither parent smokes, children have a 10% chance of smoking.
Longer Life Expectancy
A healthy smoker who smokes loses 3 months of life for every year of smoking. For this reason, smokers who quit at age 30-35 have a similar life expectancy to non-smokers.
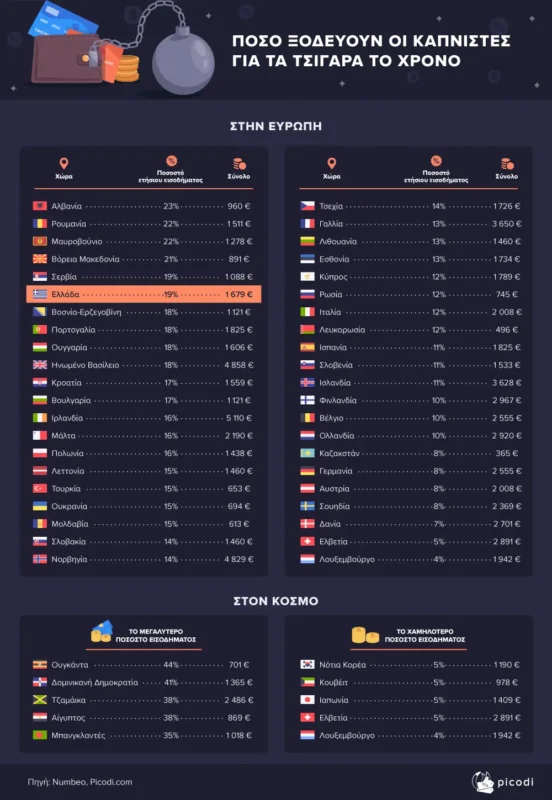
Financial bleeding for the smoker
Smoking is a financial bleed for the smoker: it robs you annually of your holidays with your family, your car payment, the rent for a better house, gifts, etc. Calculate how much money you spend annually and what you could do with it.
Smoking can be a serious financial burden for the smoker. First of all, the cost of cigarettes climbs to considerable heights as the price of cigarettes is constantly rising due to taxes and restrictive measures.
In addition to the cost of cigarettes, the smoker has to face other costs, such as those for lighters, filters and other related products. In addition, smoking increases the risk of diseases, burdening the smoker with additional medical costs for their treatment.
Finally, smokers are often subject to job losses or reduced job performance due to smoking-related health problems.
Smoking therefore represents a major economic bleed for smokers, affecting both their daily standard of living and their long-term economic security.
| Cigarettes per day | 40 | Package price | 4 |
| Daily cost | 6 | ||
| Monthly cost | 180 | ||
| Annual cost | 2190 | ||
| 10-year cost | 21900 |
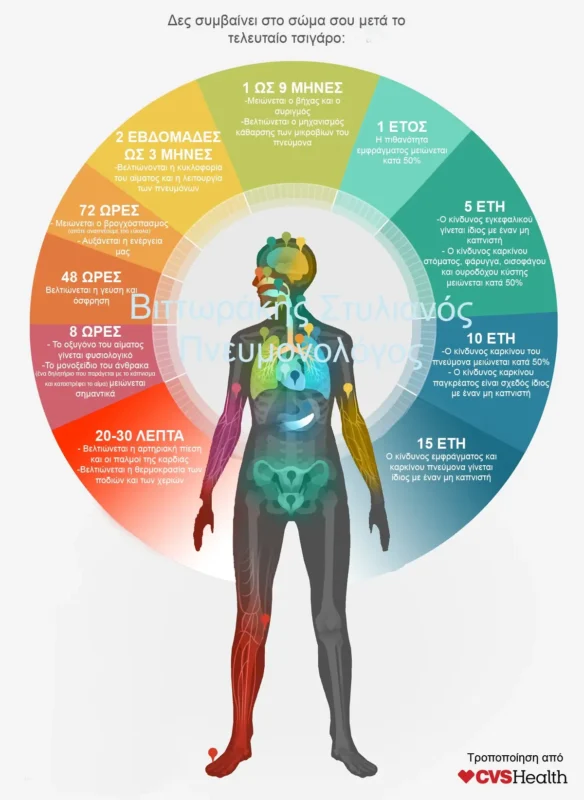
What are the Benefits of Smoking Cessation?
Once you decide to quit smoking, you open the door to a wealth of health and well-being benefits. Some of the benefits you can expect immediately after quitting smoking include:
- As soon as you quit smoking, stop on the street and smell the leaves of a tree or a rose. Taste your favorite coffee, food or drink. You’ll feel forgotten sensations again!
- By quitting cigarettes you will become more charming with your new healthy self! Statistically, you increase your attractiveness to the opposite sex who even being a smoker is more attracted to you than a non-smoker!
- You will no longer be a victim of the tobacco companies.
- You’ll be free when you don’t think about whether or not you have cigarettes before every activity! If you never have to smoke again in the cold, on a break during entertainment, hanging out of a window at work or in the kitchen of your home.
- You may see smoking as a means of relaxing from stress. but a month without a cigarette will show you how much calmer you are… What smokers call “pleasure-relaxation” is nothing more than making up for the lack of nicotine (withdrawal).
- Even if you feel that cigarettes don’t affect you physically you will be surprised at the stamina you will gain in every activity after quitting!

What is withdrawal syndrome?
It is a combination of physical and psychological symptoms that occur with smoking cessation. These include nervousness or impatience, anxiety (which may increase or decrease with smoking cessation), discomfort or depression, frustration or anger, difficulty concentrating, increased appetite or weight gain.
These symptoms are most pronounced in the first 7 days and last up to 4 weeks. The withdrawal symptoms are caused by nicotine, which is a strong addictive substance, similar to heroin and alcohol, as shown in the table below.
From the very first visit to the smoking cessation clinic, specific methods are used to assess the degree of nicotine addiction of the smoker. The administration of anti-smoking treatment practically eliminates withdrawal symptoms.
Classification of Addictive Substances (scale 1 – 3) | ||||
Substance | Medium dependence | Pleasure | Psychological dependence | Physical dependence |
| Heroin | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Cocaine | 2,39 | 3 | 2,8 | 1,3 |
| Smoking | 2,21 | 2,3 | 2,6 | 1,8 |
| Alcohol | 1,93 | 2,3 | 2,3 | 1,6 |
| Amphetamines | 1,67 | 2 | 1,9 | 1,1 |
| Cannabis | 1,51 | 1,9 | 1,7 | 0,8 |
On the Fagerström scale scores above 7 indicate an increased degree of dependence on smoking, while scores below 2 indicate a low degree of dependence. It is important to note that the interpretation of scores on the Fagerström scale is not absolute and that the degree of dependence may vary from person to person. However, higher scores usually indicate greater difficulty in quitting smoking and an increased risk of relapse after an attempt to quit. On the other hand, low scores indicate that the smoker may be more successful in quitting smoking.
How to Recognise a Smoking Addiction: Signs and Symptoms.
Smoking addiction is a serious condition that affects both the physical and mental well-being of the individual. Recognition of addiction is important in taking steps towards smoking cessation and health recovery.
How can I tell if I am an addicted to smoking?
Although all smokers have some awareness of their level of addiction, your doctor can assess your nicotine dependence based on your medical history.
There is also a way to assess dependence by specific measurements (e.g. exhaled CO) and by using some questionnaires. Most commonly we use the Fagerstrom scale which includes 6 questions. Ask your pulmonologist for more information.
The Fagerstrom Scale.
The Fagerström scale is a tool used to measure the degree of smoking addiction. It consists of questions that assess various aspects of a person’s smoking, such as frequency of smoking, desire to smoke in the morning, and ability to abstain from smoking in situations where it is prohibited.
Scoring on the Fagerström scale can help individual smokers understand their addiction and determine the most appropriate approach to quitting smoking. Usually, the higher the score on the scale, the more severe the addiction.
The information from this assessment can be used to plan a more effective smoking cessation strategy.
Fagerström Scale Indicative Questions
How quickly after you wake up do you smoke your first cigarette?
Within the first 5 minutes (3 points)
6-30 minutes (2 points)
31-60 minutes (1 point)
After 60 minutes (0 points)
Do you find it difficult not to smoke in places where smoking is not allowed? (e.g. church, libraries, cinema?)
Yes (1 point)
No (0 points)
Which cigarette is most difficult for you not to smoke?
The first cigarette of the day (1 point)
Any other cigarette (0 points)
How many cigarettes a day do you smoke?
10 or less (0 points)
11-20 (1 point)
21-30 (2 points)
31 or more (3 points)
Do you smoke more in the morning than in the afternoon
Yes (1 point)
No (0 points)
Do you smoke even when an illness forces you to stay in bed?
Yes (1 point)
No (0 points)
When should I stop smoking?
Now! It is important not to put off the decision to quit smoking. Most smokers continually put off quitting until they finally experience some of the irreversible harmful effects of smoking. Schedule your quit date within the next 4 weeks and see your pulmonologist early to help you.
How can I quit smoking?
The process of quitting smoking can be challenging, but there are many ways you can quit smoking.
- Set goals: Set clear and realistic goals for when you want to quit smoking and how you will achieve them.
- Information: Learn about the health benefits of quitting smoking and find out about the different methods available.
- Reinforcing the decision: Think about your reasons for wanting to quit smoking and reinforce your decision.
- Social support: Ask for the support of friends, family or a specialist to help you through the process.
Many people manage to quit smoking on their own, either abruptly or by gradually reducing. It is of course often difficult and for this reason it has been found that fewer than 5 in 100 people succeed on their own.
The most important thing is not to give up. The process of quitting smoking can be difficult, but it is achievable with determination, support and appropriate strategies.
SMOKING CESSATION CLINIC
The Smoking Cessation Clinic is a place where people can get specialist support and help to stop smoking. It usually involves one or more health specialists, such as doctors or psychologists, who provide one-to-one sessions or group support programmes.
How do they work?
Smoking cessation clinics operate in private practices of pulmonologists and in some hospitals. Pulmonologists involved in smoking cessation have received special training both during their specialisation and in special intensive seminars regularly organised by the Hellenic and European Respiratory Society.
The cessation clinics apply studied and specialized methods of guidance and therapeutic treatment (pharmaceutical or non-pharmaceutical) that make cessation an easy and safe reality for the patient with success rates of more than 80%.
At the smoking cessation clinic we can also easily and accurately perform the following actions:
Degree of Dependence
Estimate the degree of nicotine dependence with specific questionnaires.
Carbon Monoxide Measurement
Use a special equipment to measure the build-up of carbon monoxide (a poisonous gas produced by smoking) in your body and assess both the addiction and the significant ongoing risk you run by smoking.
Lung Function Studies
Determine the damage caused by smoking to the lungs by simple spirometry and, more specifically, by Complete Series of Lung Function Studies (appropriate equipment for these tests is available in our clinic).


What should I do before I go to my doctor to quit smoking? What changes do I need to make in my life to achieve this?
The most important step in quitting smoking is your decision. Once you seek medical help to quit smoking, your pulmonologist will help you to make this effort easier and more successful.
Before seeking medical help, it is advisable to follow the following guidelines, which will also be very useful during the quitting period:
1. Try to reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day. Try to reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke per day by reducing the number of times you smoke. When the medication starts, you will stop smoking completely according to your doctor’s instructions.
2. Reduce stress and improve your quality of life: List the causes of stress in your daily life and avoid them.
Inform your family to help you in your efforts. Capture in your memory the joy you give them by announcing your decision and remember it in every difficulty – the desire to smoke – that you will face.
Use relaxation techniques (deep- calm breathing, use something to keep your hands busy- a rosary or a wishbone) especially when you have a desire to smoke.
Avoid eating unnecessarily and, without dieting, watch your diet. Increase vegetables and fruits and limit sweet and fatty foods.
Drink plenty of water.
Increase exercise. You don’t have to start a gym if you don’t want to, just walk more, take up dance classes etc. 30 minutes of exercise a day will help maintain your weight and reduce the urge to smoke.
3. Limit time with other smokers. If another family member smokes, it is a good idea to start together or ask that no one smoke in the house or car. Avoid groups of people who smoke especially in the first month if they don’t understand your effort and get carried away.
Instructions during the period of smoking cessation
4. Recognize that moments of intense desire often lead to failure or relapse.
Avoid situations that you associate with smoking by limiting stress, alcohol, coffee or by changing habits: changing the type of coffee or beverage with another that you may not particularly like.
When you have a craving to smoke and use ‘mouth substitutes’ such as a stick of gum, slowly drink two glasses of water, a carrot, a caramel (mint or cinnamon flavoured may help more), or a cinnamon stick! Put on some music and dance if you like, walk around the block.
When you’re smoking with the newspaper or at the computer, have a pencil and keep your hands busy taking notes. You’ll be amazed at how many simple things there are to forget about cigarettes!
5. Completely put out of your mind the thought that a cigarette won’t hurt.
Nicotine causes remarkably fast changes in the brain, so that one cigarette is enough to bring you back to your previous state. Usually one cigarette is not enough and one cigarette brings another. If this happens don’t be disappointed, contact your doctor immediately. There is a solution !
6. Remember that every time you resist the urge and do not smoke, you are one step closer to getting rid of the harmful habit. Remember what you will gain if you succeed.
7. Ask for help. Your doctor will help and guide you. If you have a friend who has quit, he or she will offer you helpful advice and personal experience on ways to cope with intense cravings and will emphasize how much their life has changed since they quit. Follow his example.
On the day you decide to quit smoking you should, in addition to the above, remove all cigarettes, ashtrays and lighters you used to use from your home, car and office.
Don’t leave anything that reminds you of smoking.
Your family will support you and your friends shouldn't get carried away. If you have a desire to smoke, follow the previous instructions and use the medication as your pulmonologist told you. The medication will almost completely reduce the withdrawal symptoms, which are most severe in the first week and disappear in 3-4 weeks. Always keep in mind that this is made easier if you don't smoke a single cigarette and that the quit effort will be a one-time, life-changing effort.
Are there any medicines to help me?
There are several medications available today that will help you quit smoking without difficulty. They are extremely safe when given under medical supervision but are not needed for all patients.
Do not improvise without a recipe
More importantly, these drugs “don’t work” for every patient and should not be taken without a prescription because they helped someone you know. Only your smoking cessation specialist pulmonologist can recommend that you receive, if necessary, the appropriate and specific treatment for you.
Do not improvise by taking your own medicines.
Other Smoking Cessation Methods
Electronic cigarettes:
In recent years they have been promoted for commercial reasons as safe substitutes for cigarettes and have even had a high penetration especially among young people.
They should be avoided as they are marketed and are proven to be ineffective and there are now many studies proving their harmful effects.
For example, many e-cigarettes have been found to release substances that are carcinogenic (e.g. diethylene glycol a car antifreeze liquid), or unexpected (aminotadalafil, rimonabant, cannabis, vodka), or finally contain nicotine at toxic levels.
Studies have also shown that they negatively affect lung function, as measured by modern spirometers, and have recently been found to predispose to serious infections and complications (fluid in the lung – pleural effusion).
Even if they are ever modified and made safe, with clear content and dosage, they should not be taken without monitoring.
After all, it is not right to replace one harmful habit and negative pattern with other potentially less harmful ones.
Acupuncture:
Although studies have not proven its effectiveness, if you are participating in a program, don’t smoke, and feel that acupuncture is helping you, it is not necessary to stop. Besides, the “placebo” (placebo-psychological) effect of any method is welcome if it has positive results.
Similarly, there is no evidence whatsoever that methods such as laser therapy, pressure therapy, electrostimulation and hypnosis help to stop smoking.
Smoking in Special Cases
Smoking affects the health of people of all ages and in all social groups, but some specific circumstances may be even more vulnerable to the effects of smoking. These cases include:
Breastfeeding:
There is no such thing as a non-harmful cigarette in pregnancy Smoking, whether active or passive, is a risk to your baby. Since cigarettes are a drug it is difficult to quit smoking and pregnant women must seek for medical help if the cannot quit smoking. Pregnancy is a unique opportunity to get rid of smoking.
Smoking is also not allowed during breastfeeding. Even the smell of your clothes from cigarettes are harmful substances inhaled by your baby.
Teens:
If you have been a smoker from such a young age, it is necessary to quit because the problems from smoking will appear quite early.
Although the risk of smoking is now known to everyone, and especially to the various media-informed teenagers nowadays, at this age the risk of a future condition seems very remote.
However, if you smoke, you should not forget that smoking spoils your beauty (yellow teeth, fingers, bad smell in your clothes and mouth, and your skin) and completely destroys your pocket money and your ability to do other things with your friends. Besides, you know that today ‘smart’ – is the one who doesn’t smoke!
Parents should also set an example for their children and not smoke. Don’t forget that 80% of children who smoke have parents who smoke.
Older siblings who do not smoke can also set an example. In addition, it is important to inform the child from an early age both at home and at school.
I Finished the Treatment and I don't Smoke Anymore!
Congratulations, you managed to stop smoking! You have been relieved of an unbearable cost to your pocket and your health. You are an example for your friends and children. Always remember that a cigarette can be the cause of relapse and never give in to temptation no matter how enjoyable it is. Now that you know that no cigarette solves problems but adds new ones, face the difficulties without smoking.